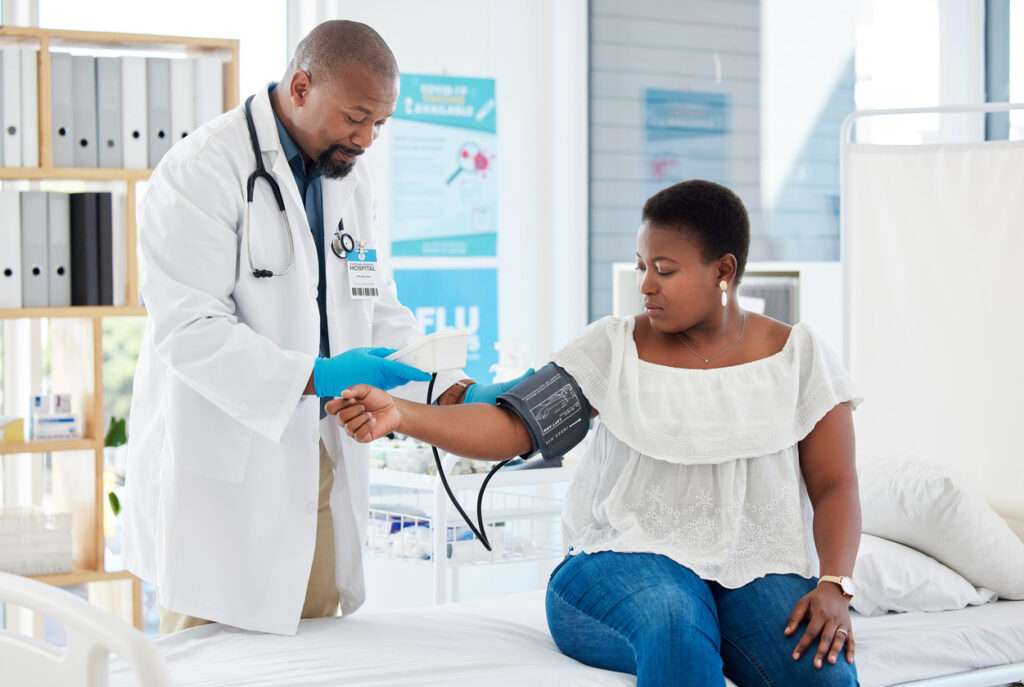
Women’s Health Month is observed in May and focuses on promoting awareness about health issues specific to women. During this month, the aim is to encourage women to prioritize their health and well-being by providing information, resources, and support on a variety of topics, including:
- Preventive Care: Emphasizing the importance of regular health screenings such as mammograms, Pap smears, and bone density tests.
- Reproductive Health: Providing education on contraception, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.
- Mental Health: Highlighting the importance of mental well-being and addressing issues such as depression, anxiety, and stress.
- Chronic Conditions: Raising awareness about conditions that predominantly affect women, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and autoimmune diseases.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Encouraging a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and healthy habits to prevent diseases and enhance quality of life.
Women’s health is critically important because it directly impacts the well-being of families, communities, and societies at large. Here are several key reasons why prioritizing women’s health is essential:
- Reproductive and Maternal Health: Ensuring women have access to adequate healthcare during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum can significantly reduce maternal and infant mortality rates and promote healthy development.
- Chronic Disease Management: Women are at higher risk for certain chronic conditions like breast cancer, osteoporosis, and autoimmune diseases. Early detection and effective management of these conditions can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
- Mental Health: Women are more likely than men to experience depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Addressing these concerns is crucial for overall well-being and can prevent more severe health problems.
- Preventive Care: Regular health screenings and preventive measures can detect health issues early, leading to more effective treatment and better outcomes. This can reduce healthcare costs and improve longevity.
- Economic Impact: Healthy women are more likely to participate in the workforce, contributing to economic stability and growth. Poor health can lead to increased absenteeism, lower productivity, and higher healthcare costs.
- Social and Family Roles: Women often serve as primary caregivers in families. Their health directly affects their ability to care for children, elderly parents, and other family members, thereby influencing the overall health and well-being of entire households.
- Health Disparities: Addressing women’s health issues helps to close gender gaps in healthcare access and quality. This includes ensuring women receive equitable treatment and resources regardless of their socio-economic status, race, or geographic location.
Women can prioritize their health by adopting a holistic approach that includes regular medical care, a balanced lifestyle, and proactive health management. Here are several effective strategies:
- Regular Health Screenings: Stay up-to-date with annual check-ups and recommended screenings such as mammograms, Pap smears, bone density tests, and blood pressure checks. Early detection of issues can lead to better outcomes.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities like walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga.
- Mental Health Care: Prioritize mental well-being by managing stress, practicing mindfulness or meditation, seeking therapy if needed, and maintaining social connections.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support overall health, including immune function, mental clarity, and emotional stability.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain hydration, which is vital for bodily functions and energy levels.
- Reproductive Health: Stay informed about reproductive health and seek appropriate care. This includes regular gynecological exams, understanding contraceptive options, and addressing any menstrual or menopausal concerns.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Limit alcohol consumption, avoid smoking, and stay away from recreational drugs. These habits can have significant long-term health consequences.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or asthma, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest health information and guidelines. Knowledge about health trends, emerging research, and preventive measures can empower you to make informed decisions.
- Self-Care Practices: Incorporate self-care into your routine, whether through hobbies, relaxation techniques, or spending time doing activities you enjoy.
- Vaccinations: Ensure vaccinations are current, including those for the flu, HPV, and other preventable diseases.
By integrating these practices into daily life, women can take charge of their health, reduce the risk of disease, and enhance their overall quality of life.